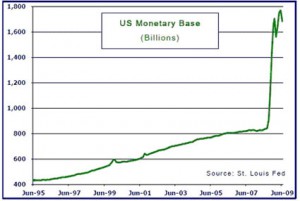
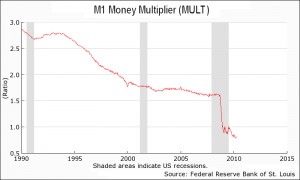
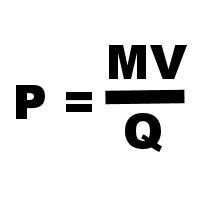In the field of economics, many experts agree that the long-term effects of inflation are dependent on the money supply in a country. Alternatively, the price levels are directly proportional to the money supply in the long run. Therefore, the money supply or the currency in circulation can directly affect the prices of goods and services. The confusion arises because both monetary inflation (an increase in the money supply) and price inflation (an increase in consumer prices) are both commonly referred to as "inflation". Even though many people consider money printing to be the cause of more money in circulation, physical paper in circulation is actually only a small percentage of the … [Read more...]
The Effects of Inflation and Interest Rates on Commodity Prices
In common usage, inflation refers to steadily rising prices of goods and services over time, while "deflation" relates to falling prices. Inflation is both a boon and a bane to the economy and the rate of inflation is affected by a variety of factors including FED monetary policy, interest rates, supply vs. demand, and the Velocity of money. However, strictly speaking, rising prices are "price inflation" which is generally caused by "monetary inflation" i.e. the expansion of the money supply, among other things. See What is Inflation? for more info. Many Keynesian Economists believe that Inflation is a prerequisite for economic growth and prosperity and Keynesians believe Monetary … [Read more...]
The Quantity Theory of Money
We have written quite extensively on the cause of inflation in articles like: How does the Money Supply affect our Inflation Rate? in What is Inflation? and Inflation Cause and Effects. One of the keys to understanding inflation is the Money Multiplier. Because of the "Fractional Reserve system banks are only required to keep a small fraction of the money on deposit as "reserves" against potential withdrawals the bank can loan out the majority of the money on deposit to earn interest. This results in a multiplication effect increasing the money supply by vast multiples. This "leverage" can work in either direction. In April 2010, I wrote an article explaining how this can result in … [Read more...]
Inflation or Deflation? – Yes
Over the years we've published a variety of articles on the inherent "tug-of-war" between inflationary and deflationary forces in the world including How can we have Inflation and Deflation at the same time? and Battle of the 'Flations both from back in 2008 and Deflation or Inflation - Which is it? in 2009 and Which is Stronger- Inflation or Deflation? in 2010. Another recurring theme has been Velocity of Money and Money Multiplier- Why Deflation is Possible and today John Mauldin will take a stab at each these critical topics once again. Understanding their interrelationships will greatly help you understand the monetary forces at work.~ Tim McMahon, editor The Flat Debt Society By … [Read more...]
Pushing on a String, Velocity of Money and Money Multiplier Conspire Against the FED
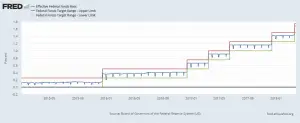
Under certain circumstances such as high national indebtedness, fear of bad economic times or when interest rates approach zero, monetary policy becomes ineffective in enticing consumers into spending more money. Economists refer to this as "Pushing on a String" because if the basic demand doesn't exist to induce people to spend money, it can't be forced through monetary policy. Prime examples of this are during the Great Depression in the United States and in Japan since the 1990s. And as Lacy Hunt explains we are once again facing this problem in the United States since 2008. ~Tim McMahon, editor Federal Reserve Policy Failures Are Mounting By Lacy H. Hunt, Ph.D., Economist The Fed's … [Read more...]
Is Ben Bernanke “Shooting Blanks”?
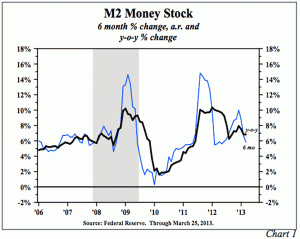
Summary: Lacy Hunt and Van Hoisington launch into their first-quarter "Review and Outlook," this week with a statement that some may find eye-opening: "The Federal Reserve (Fed) is not, and has not been, 'printing money'…" But given the facts of life about how money is really created (and destroyed), they are of course right: it's all about the acceleration – or deceleration – in the M2 money supply. Van and Lacy say, "A review of post-war economic history would lead to a logical assumption that the money supply (M2) would respond upward to [the Fed's] massive infusion of reserves into the banking system. Mystery Math- Monetary Base up 350%, M2 Up 35%? And yet, the Fed's 3.5x … [Read more...]
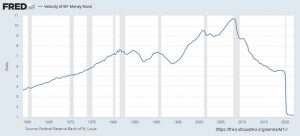
Velocity of Money
What is the velocity of money? Simply defined, the velocity of money is the turnover in the money supply. A shop owner can measure how fast his inventory is selling by calculating "inventory turnover." To do that, he simply calculates Total Sales ÷ Average Inventory for the period in question. See: Inventory TurnOver for more information. But if you expand the idea of turnover to the entire country, you get the "Velocity of Money". Strictly speaking all the velocity of money tells us is how long people hold onto their money. But from that we can infer their motives and perceptions of the economy in general... The Velocity of Money Calculation To Calculate the Velocity of Money, you … [Read more...]
Inflation and Velocity of Money
How do you define inflation? In some ways it's a slippery thing, like trying to nail Jell-O to a tree. One common definition amounts to "a general and sustained rise in the price of goods and services." Another is "a persistent decline in the purchasing power of money." Others argue that inflation is directly tied to the money supply. That is to say, they believe a substantial rise in the money supply is the same thing as inflation. (This is one small step removed from Milton Friedman’s old assertion: "Inflation is always and everywhere a monetary phenomenon.") Why is the debate important? Because of the infamous chart you see below (courtesy of hedge fund QB Partners and the St. Louis … [Read more...]
Velocity of Money and Money Multiplier- Why Deflation is Possible
By Tim McMahon Back in 1924, John Maynard Keynes called gold a barbarous relic. There is a thought prevalent these days that deflation is the new barbarous relic. In a speech in November of 2002, Federal Reserve chairman Ben Bernanke said, “I believe that the chance of significant deflation in the United States in the foreseeable future is extremely small… I am confident that the Fed would take whatever means necessary to prevent significant deflation… the effectiveness of anti-deflation policy could be significantly enhanced by cooperation between the monetary and fiscal authorities.” He went on to say, “the U.S. government has a technology, called a printing press (or, today, its … [Read more...]